

Impress Guide 7.2
Chapter 2
Master Slides, Styles, and Templates
This document is Copyright © 2021 by the LibreOffice Documentation Team. Contributors are listed below. This document maybe distributed and/or modified under the terms of either the GNU General Public License (https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html), version 3 or later, or the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), version 4.0 or later.
All trademarks within this guide belong to their legitimate owners.
To this edition
|
Peter Schofield |
Vasudev Narayanan |
Rachel Kartch |
|
Peter Schofield |
Felipe Viggiano |
Regina Henschel |
|
Dimona Delvere |
Michele Zarri |
T. Elliot Turner |
|
Jean Hollis Weber |
Low Song Chuan |
Hazel Russman |
Please direct any comments or suggestions about this document to the Documentation Team’s mailing list: documentation@global.libreoffice.org
Note
Everything sent to a mailing list, including email addresses and any other personal information that is written in the message, is publicly archived and cannot be deleted.
Published October 2021. Based on LibreOffice 7.2.
Some keystrokes and menu items are different on macOS from those used in Windows and Linux. The table below gives some common substitutions for the instructions in this document. For a detailed list, see the application Help.
|
Windows or Linux |
macOS equivalent |
Effect |
|
Tools > Options |
LibreOffice > Preferences |
Access setup options |
|
Right-click |
Control+click or right-click depending on computer setup |
Open a context menu |
|
Ctrl (Control) |
⌘ (Command) |
Used with other keys |
|
F11 |
⌘+T |
Open the Styles deck in the Sidebar |
In addition to careful planning of the content, as discussed in Chapter 1 Introducing Impress, planning the appearance of the presentation is important. It is best to do this after developing an outline, because the outline determines some of the requirements for the appearance of the slides. For example:
What color combinations (background and text) will look good and also be easy for an audience to read?
Would an image help an audience understand the contents better?
Is there any particular text and image that has to appear on all the slides? For example a company name and logo.
Would an audience benefit from having the slides numbered so that they can quickly refer to one of them?
Is a background graphic or gradient required? If so, select something that does not interfere or clash with content such as the colors used in charts.
Is one or more master slide required?
Will one slide design suit all of the presentation content?
The appearance of slides can be changed as the presentation is developed, but planning ahead saves time in the long run.
A master slide is a slide that is used as the starting point for other slides. It is similar to a page style in LibreOffice Writer as it controls the basic formatting of all slides based on it. A presentation can have more than one master slide.
Note
LibreOffice uses three terms for one concept: master slide, slide master, and master page. All refer to a slide which is used to create other slides. This user guide uses the term master slide, except when describing the user interface.
A master slide has a defined set of characteristics, including the background color, graphic, or gradient. It also can include objects (for example, logos, decorative lines) in the background; headers and footers; placement and size of text frames; and text formatting.
All of the characteristics of master slides are controlled by styles. The styles of any new slide created are inherited from the master slide from which it was created. In other words, the styles of the master slide are available and applied to all slides created from that master slide. Changing a style in a master slide results in changes to all the slides based on that master slide. It is, however, possible to modify each individual slide without affecting the master slide.
Note
It is highly recommended to use the master slides whenever possible. However, there are occasions where manual changes are needed for a particular slide. For example, editing an individual slide to enlarge the chart area when the text and chart layout is used.
Master slides have two types of styles associated with them: presentation styles and drawing styles. The presentation styles can be modified, but new presentation styles cannot be created. For drawing styles, the styles can be modified and new drawing styles can be created. For more information, see “Working with styles”.
Impress comes with a collection of master slides. These master slides are shown in the Master Slides deck of the Sidebar (Figure 1). This deck has three panels: Used in This Presentation, Recently Used, and Available for Use. Click the expand marker next to the name of a panel to expand it and show thumbnails of the master slides, or click the collapse marker to collapse the section to hide the thumbnails.
Each of the master slides shown in the Available for Use panel is from a template of the same name. These presentation templates are included when LibreOffice is installed on a computer. If templates have been created, or added from other sources, master slides from those templates also appear in this list. See “Working with templates” for more information about templates.
If a new presentation is being created without using one of the templates available then a default master slide is available (see Chapter 1, Introducing Impress for more information). This default master slide is a good starting point for creating master slides. An example of the default master slide is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 1: Master Slides deck on Sidebar
Figure 2: Default master slide

Figure 3: Master View toolbar
Figure 4: Rename Master dialog
Creating a new master slide is carried out when Impress is in Master View.
1) Go to View > Master Slide on the Menu bar to open Master View in the Workspace. The Master View toolbar also opens (Figure 3). If the Master View toolbar does not open, go to View > Toolbars on the Menu bar and select Master View.
2) Create a new master slide using one of the following methods and a new master slide appears in the Slide Pane:
Click on New Master in the Master View toolbar.
Right-click on a master slide in the Slide Pane and select New Master from the context menu.
Go to Slide > New Master on the Menu bar.
3) Rename the new master slide using one of the following methods and open the Rename Slide dialog (Figure 4):
Click on Rename Master in the Master View toolbar.
Right-click on the new master slide in the Slide Pane and select Rename Master from the context menu.
4) Enter a memorable name for the new master slide in the Name text box, then click on OK to save the changes and close the dialog.
5) Make sure the new master slide is selected in the Slide Pane and add all the text, graphics and master elements that required for the new master slide. The chapters in this user guide give more information on adding, editing, formatting and managing the different types of objects on a master slide.
6) When finished creating a new master slide, use one of the following methods to return to Normal View:
Click on Close Master View on the Master View toolbar.
Go to View > Normal on the Menu bar.
7) Save the presentation file before continuing.
To apply a master slide to all slides or selected slides in a presentation:
1) Click on Master Slides to open the Master Slides deck on the Sidebar.
2) Right-click on the master slide required in the Used in This Presentation section in the Master Slides deck on the Sidebar.
3) Select Apply to All Slides or Apply to Selected Slides from the context menu.
In a presentation, it maybe necessary to mix multiple master slides that belong to different templates (for more information, see “Working with templates”). For example, use a completely different layout for the first slide of the presentation, or add a slide from a different presentation.
1) Select the slide or slides in the Slide Pane where the master slide is to be changed.
2) Go to Slide > Change Slide Master on the Menu bar to open the Available Master Slides dialog (Figure 5).
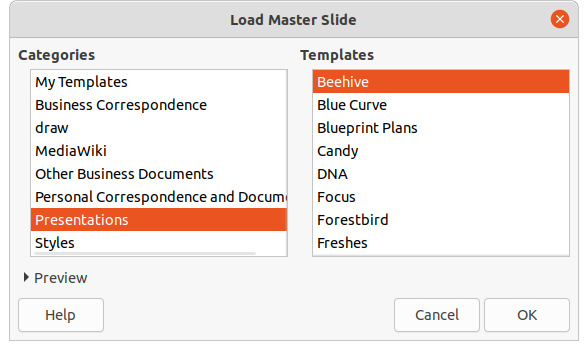
3) To add master slides, click on Load to open the Load Master Slide dialog (Figure 6).
4) In the Load Master Slide dialog, select the template category and the template from which to load the master slide
5) Click OK to close the Load Master Slide dialog and the master slides from the selected template appear in the Available Master Slides dialog.
6) Select the master slide required in Select a Slide Design box.
7) To apply the selected master slide to all slides in a presentation, select the Exchange background page check box.
8) To apply the slide design to the selected slides only, deselect the Exchange background page check box.
9) Click OK to apply the selection to the slides and close the Available Master Slides dialog.
Figure 5: Available Master Slides dialog
Figure 6: Load Master Slide dialog
The following items can be changed on a master slide:
Background (color, gradient, hatching, or bitmap). For more information, see “Selecting and applying backgrounds”.
Background objects (for example, adding a logo or decorative graphics). For more information, see “Adding images”; Chapter 4, Adding and Formatting Pictures; Chapter 5, Managing Graphic Objects; and Chapter 6, Formatting Graphic Objects.
Text attributes for the main text area and notes. For more information, see “Adding text and fields” and Chapter 3, Adding and Formatting Text.
Size and placement of default frames for slide titles and content. For more information, see “Default text areas”.
Size, placement, and contents of header and footer elements to appear on every slide. For more information, see “Adding text and fields” and Chapter 3, Adding and Formatting Text.
Editing a master slide is as follows:
1) Select View > Master Slide from the Menu bar. This also opens the Master View toolbar.
2) Select a master slide for editing in the Slide Pane so that it appears in the Workspace (Figure 7).
3) Go to Slide > Slide Properties on the Menu bar or right-click in the Workspace and select Slide Properties from the context menu to open the Slide Setup dialog (Figure 8).
4) Use the various options in the Slide, Background and Transparency pages in the Slide Setup dialog to make changes to the master slide format.
5) Click OK to save the changes and close the Slide Setup dialog.
Figure 7: Master slide view
Figure 8: Slide Properties dialog
6) Select an object on the master slide, then right-click on the object to open a context menu.
7) Select one of the options from the context menu to edit the object. Selecting an option may open another context menu, a dialog, an application or file browser window to make the necessary changes to a selected object.
8) Click on Close Master View on the Master View toolbar or go to View > Normal on the Menu bar to exit from editing master slides.
9) Save the presentation file before continuing.
Note
Any changes made to a master slide in Master Slide view appear on all slides using the same master slide. Always make sure to close Master Slide view and return to Normal view before working on any of the presentation slides.
Any changes made to any object on a slide in Normal view (for example, changes to bullet point style, color of the title area, and so on) will not be overridden by subsequent changes made to the master slide used for that slide. However, where it is desirable to revert the formatting of a manually formatted object on a slide to the style defined in the master slide, select the object on the slide and use one of the following methods to change the formatting:
Go to Format > Clear Direct Formatting on the Menu bar.
Right-click on an object and select Clear Direct Formatting from the context menu.
Note
The title and text boxes inherit the properties of a master slide, but if the position of these text boxes in the master slide has changed, the layout may appear corrupted. Some of the layout elements may have to have the horizontal and/or vertical manually repositioned on a slide.
Backgrounds can be applied to a number of elements in Impress (for example: slide, default text area, image and so on). The procedure is similar when applying a background to a slide or an object.
1) Select View > Master Slide from the Menu bar. This also opens the Master View toolbar.
2) Select a master slide in the Slide Pane so that it appears in the Workspace.
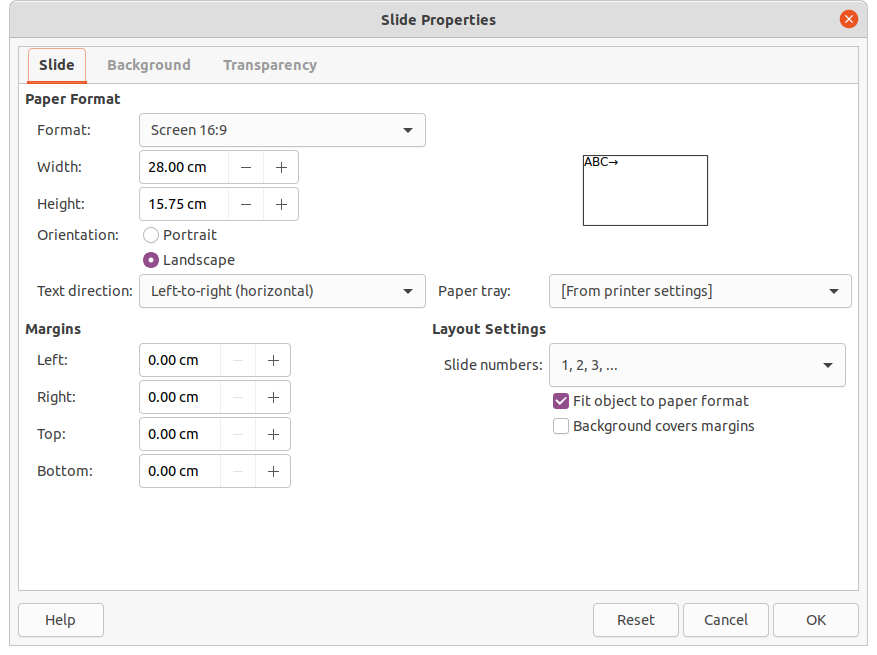
3) Go to Slide > Slide Properties on the Menu bar or right-click in the Workspace and select Slide Properties from the context menu to open the Slide Setup dialog.
4) Select the Background tab to open the Background page on the Slide Properties dialog (Figure 9).
5) Select the type of background required from Color, Gradient, Bitmap, Pattern and Hatch. See Chapter 6, Formatting Graphic Objects for more information on how to use the options available for each type of background selected.
6) When satisfied with the slide background, click OK to save the changes and close the Slide Setup dialog.
1) Select View > Master Slide from the Menu bar. This also opens the Master View toolbar.
2) Select a master slide in the Slide Pane so that it appears in the Workspace.
Figure 9: Slide Setup dialog - Background page
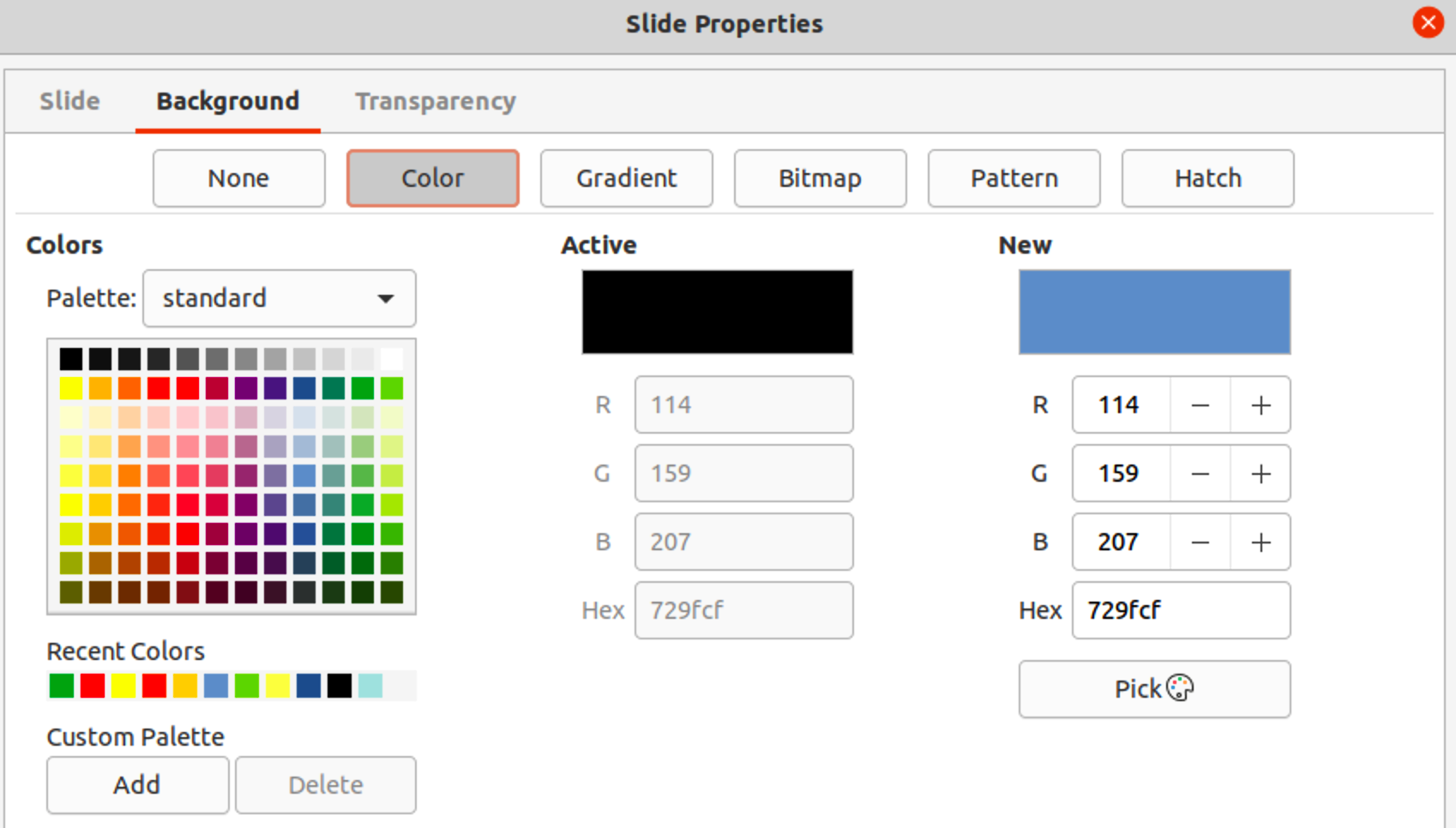
Figure 10: Presentation styles in Styles deck on Sidebar
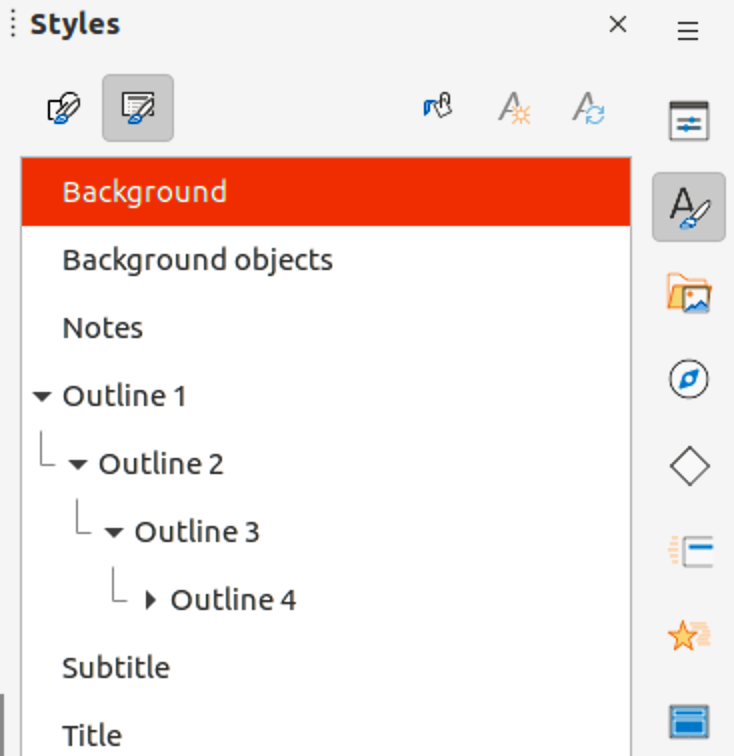
3) Click on Styles on the Sidebar to open the Styles deck.
4) Click on Presentation Styles on the Styles deck to open the Presentation Styles list (Figure 10).
5) Right-click on Background style and select Modify from the context menu to open the Background dialog. This dialog only has one tab (Area) and offers the same options as the Background page in the Slide Setup dialog.
6) Select the type of background required from Color, Gradient, Bitmap, Pattern and Hatch. See Chapter 6, Formatting Graphic Objects for more information on how to use the options available for each type of background selected.
7) When satisfied with the background, click OK to save the changes and close the Background dialog.
Tip
Custom fills can be created for each type of background. See Chapter 6, Formatting Graphic Objects for more information on creating custom fills for each type of background.
When the same image is to appear on every slide of a presentation, the easiest and quickest solution is to use the master slide. This saves time while creating a presentation, allowing modification or repositioning of the image on all slides. If the same image is added to each slide manually, modification and repositioning have to be performed on each individual slide in a presentation. In addition to images, a number of other objects can be added to the background, for example decorative lines, text, and shapes.
LibreOffice supports a large number of image and graphic formats. For more information on working with images, see Chapter 4, Adding and Formatting Pictures; Chapter 5, Managing Graphic Objects; and Chapter 6, Formatting Graphic Objects.
For example, one of the most common actions in preparing a presentation is to add an image to the master slide. To insert an image already available on the computer, follow these steps:
1) Select View > Master Slide from the Menu bar. This also opens the Master View toolbar.
2) Select the master slide where the image is to be added.
3) Select Insert > Image on the Menu bar to open the file browser.
4) Navigate to the directory where the image is located and select it.
5) Click Open to close the file browser and the image is placed centrally into the master slide.
6) If necessary, modify and/or reposition the image on the master slide.
7) Right-click on the image and select Arrange > Send to Back from the context menu. This moves the image to the background so that any information added to the slide when creating a presentation appears over the background image.
Note
LibreOffice offers the option to insert an image as a link to the file rather than embedding it in a presentation. This is only useful when a presentation is not intended for distribution onto other computers and it will remain in the same computer and directory structure. For example, it could be created on a notebook computer, which is then used to give the presentation to a group of clients.
However, if the presentation file is to be distributed to other computers, the image must be embedded to avoid the “missing image” syndrome when the presentation is given using a different computer.
When a master slide is opened for editing, it contains five default text areas, as shown in Figure 2.
Title area for AutoLayouts.
Object area for AutoLayouts.
Date area.
Footer area.
Slide number area.
Click in any of these areas to display the selection handles around the default text area. Use these selection handles to modify the size and position of a default text area.
1) Select the default text area for repositioning so that the selection handles are visible.
2) Move the cursor toward the border of the default text area, not on a selection handle, and the cursor changes shape. The cursor shape (normally a clenched hand) is dependent on the computer setup .
3) Click and drag the default text area to the desired position, then release the left mouse button.
4) Position the cursor over a left or right selection handle.
5) Click and drag the left or right selection handle to change the width of the default text area.
6) Position the cursor over a top or bottom selection handle.
7) Click and drag the top or bottom selection handle to change the height of the default text area.
8) Position the cursor over a corner selection handle.
9) Click and drag the corner selection handle to change both the height and width of the default text area at the same time.
10) Release the mouse button when the default text area is the required width or height.
Note
The shape of the cursor usually changes when positioned over a selection handle giving a clear visual indication of how it will affect the shape of the default text area when the selection handle is moved.
Tip
Keep the Shift key pressed while dragging a selection handle to maintain the ratio between the width and height dimensions of the default text area.
Figure 11: Position and Size dialog
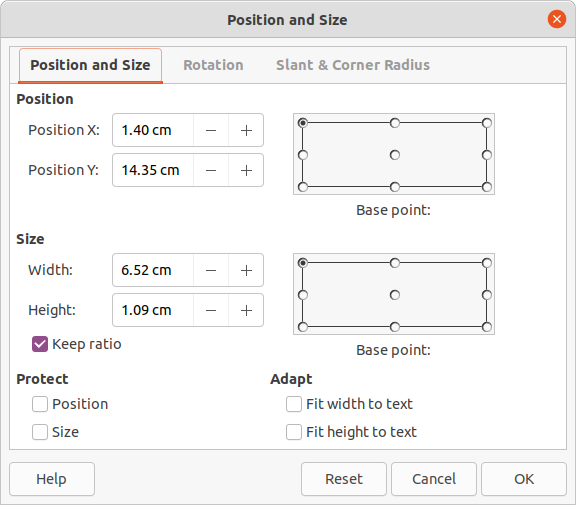
To accurately control the shape, size and position of a default text area, it is recommended to use the Position and Size dialog or the Position and Size panel in the Properties deck on the Sidebar.
1) Select the default text area by clicking on its border.
2) Use one of the following methods to access the position and size options for a default text area:
Go to Format > Object and Shape > Position and Size on the Menu bar to open the Position and Size dialog (Figure 11).
Use the keyboard shortcut F4 to open the Position and Size dialog.
Right-click on the border of the default text area and select Position and Size from the context menu to open the Position and Size dialog.
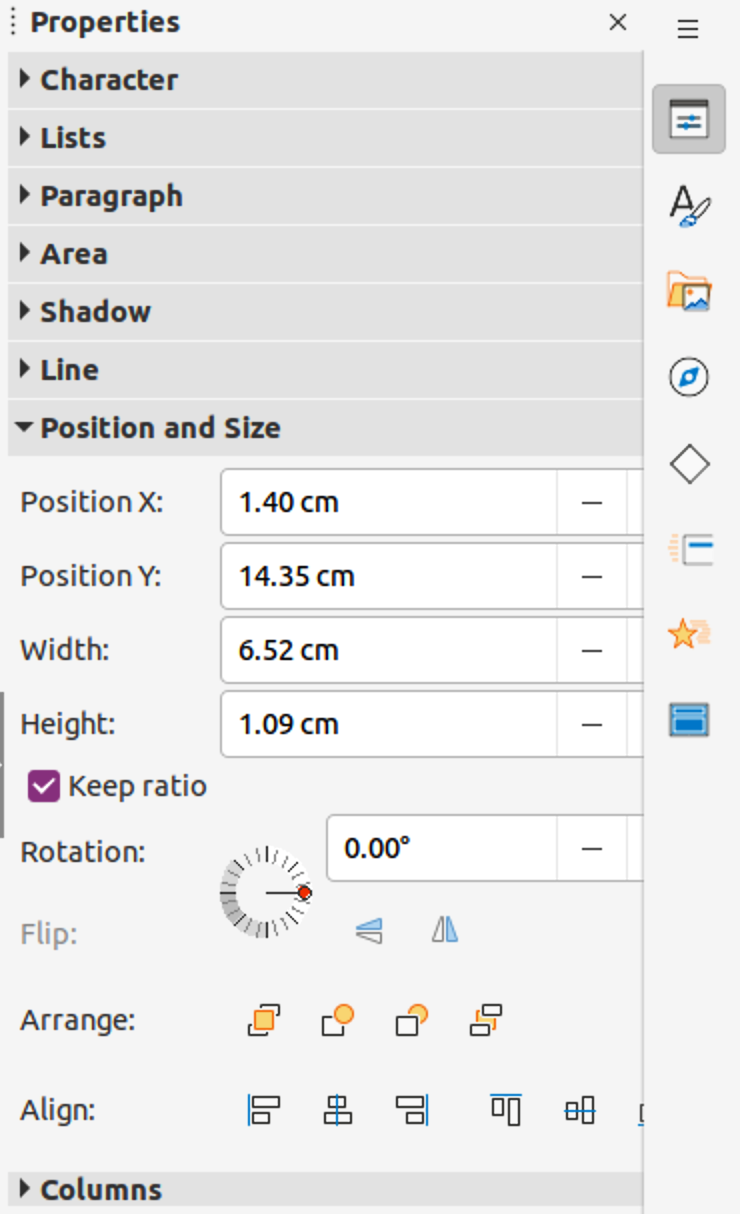
Click on Properties on the Sidebar to open the Properties deck, then open the Position and Size panel (Figure 12).
Figure 12: Position and Size panel in Properties deck on Sidebar
The Position and Size options are explained fully in the Draw Guide. Only short descriptions of the most important functions are provided as follows:
Use Position to specify the X (horizontal) and Y (vertical) position of the default text area. The values represent the distance of the selected base point and the default position is the top left corner of the slide.
Use Size to specify the width and height of the default text area.
In the Position and Size dialog only, Base point allows selection of a point on the rectangular area that does not move while resizing. The default setting of top left corner means that the position of the top left corner of the area will not change after resizing.
Use Rotation to rotate the default text area. For example, place the footer area on the side by rotating each text area by 90 degrees obtain a more modern layout. In general it is preferable to use only horizontal or vertical orientation for ease of editing, although the program does not impose restrictions on the values that can be used.
Use Slant & Corner Radius to add a corner radius to a text box border only if a visible line style has been selected. The slant options are only available for images or shapes.
Change the type of area fill used for backgrounds in a default text area using one of the following methods. The options available depend on the type of area fill selected. See Chapter 6, Formatting Graphic Objects for more information on changing backgrounds.
Go to Format > Object and Shape > Area on the Menu bar to open the Area dialog (Figure 13).
Right-click on the default text area and select Area from the context menu to open the Area dialog.
Click on Properties on the Sidebar to open the Properties deck, then open the Area panel (Figure 14).
Figure 13: Area dialog
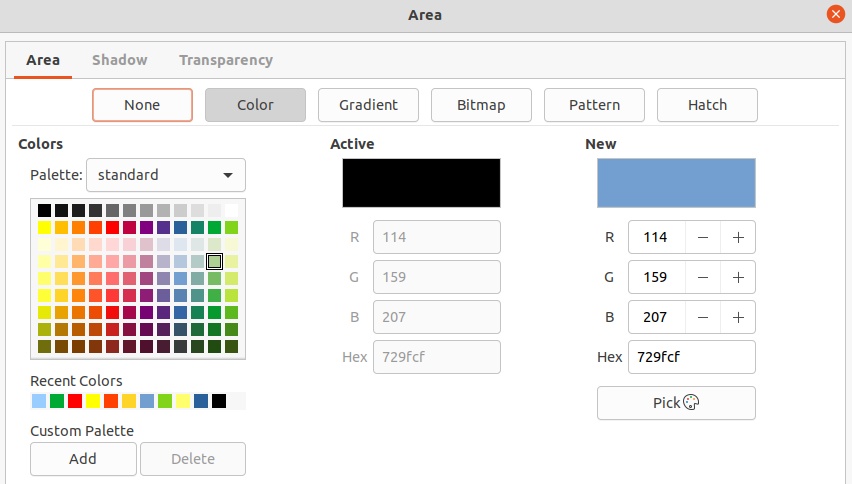
Figure 14: Area panel in Properties deck on Sidebar
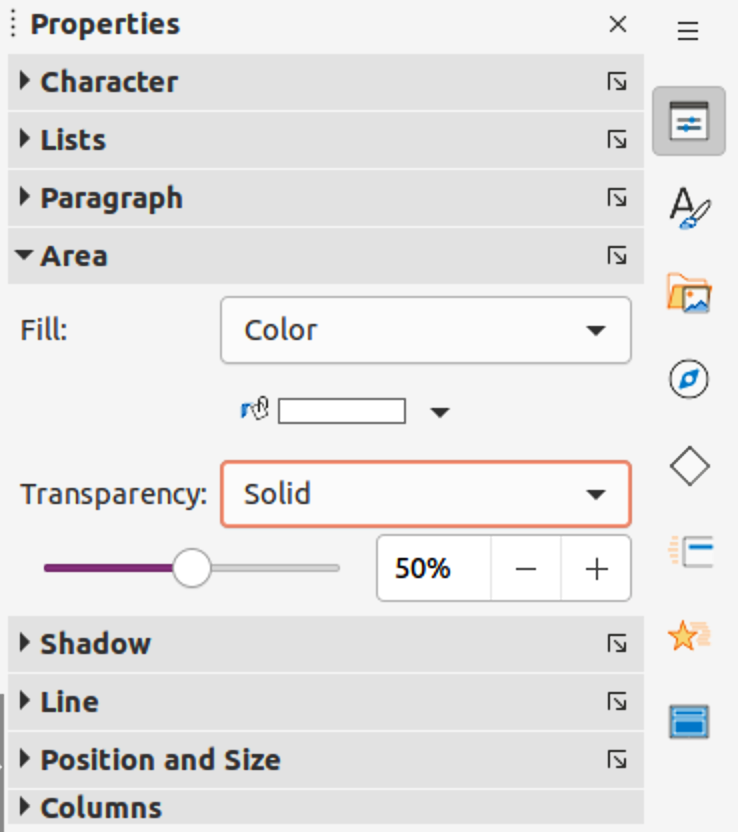
Figure 15: Line dialog
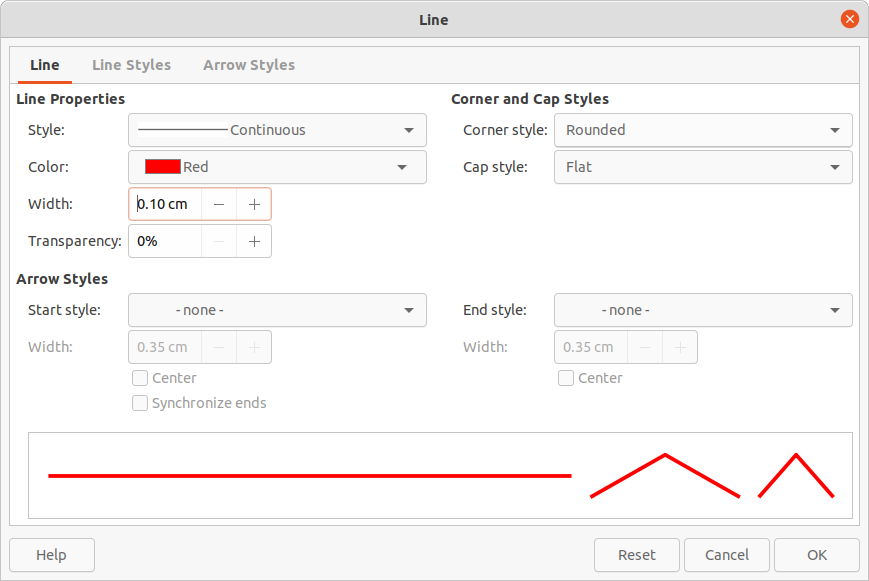
Figure 16: Line panel in Properties deck on Sidebar
Change the type of line used for borders in a default text area using one of the following methods. The options available in this dialog depend on the type of line selected. See Chapter 6, Formatting Graphic Objects for more information on changing borders.
Go to Format > Object and Shape > Line on the Menu bar to open the Line dialog (Figure 15).
Right-click on the object and select Line from the context menu to open the Line dialog.
Click on Properties on the Sidebar to open the Properties deck, then open the Line panel (Figure 16).
Change the alignment of default text area in relation to its position on a master slide or the alignment between a default text area and other objects on a master slide using one of the following methods. See Chapter 5, Managing Graphic Objects for more information on changing alignment of default text areas.
Go to Format > Align Objects on the Menu bar and select the type of alignment from the options available in the context menu.
Right-click on the object and select Align Objects from the context menu, then select the type of alignment from the options available in the context menu.
Click on the triangle ▼ to the right of Align Objects on the Line and Filling toolbar and select the type of alignment from the options available.
Select the required alignment tool in the Position and Size panel in the Properties deck on the Sidebar.
Arrange the position of an object on a slide in relation to other objects on a slide using one of the following methods. See Chapter 5, Managing Graphic Objects for more information on changing position of default text areas in relation to other objects.
Go to Format > Arrange on the Menu bar and select the type of arrangement from the options available in the context menu.
Right-click on the object and select Arrange from the context menu, then select the type of arrangement from the options available in the context menu.
Click on the required arrangement tool on the left end of the Line and Filling toolbar.
Select the required arrangement tool in the Position and Size panel on the Properties deck on the Sidebar.
Adding text and fields to a master slide allows placing of information that appears on all the slides of a presentation. For example, presentation title, company name and logo, date, and slide number. For more information on adding and formatting text and fields, see Chapter 3, Adding and Formatting Text.
Text objects can be placed anywhere on the master page and appear on every slide in a presentation. Text objects can also be placed in the footer if the default fields in the footer of a presentation are not going to be used.
1) Select View > Master Slide from the Menu bar to open the master slide view. This also opens the Master View toolbar.
2) Select the master slide so that it appears in the Workspace.
3) Switch text editing mode on using one of the following methods. The Text Formatting toolbar (Figure 17) automatically opens replacing the Line and Filling toolbar.
Select Insert Text Box on the Standard or Drawing toolbar.
Go to Insert > Text Box on the Menu bar.
Use the keyboard shortcut F2.
4) Click once on the master slide so that a text box is created and there is a flashing cursor inside the text box.
5) Type or paste the text into the text object, then format the text. See Chapter 3, Adding and Formatting Text for more information.
6) Click outside the text object to close the Text Formatting toolbar and reopen the Line and Filling toolbar.
7) Click Close Master View on the Master View toolbar or go to View > Normal on the Menu bar when adding and formatting text to a master slide is completed.
Figure 17: Text Formatting toolbar
By default, the footer used in a slide consists of three sections with each section containing a default field as follows:
Left section – date and time, labelled Date Area. Field name is <date/time>.
Center section – footer text, labelled Footer Area. Field name is <footer>. This section can be used for the presentation title, file name and so on.
Right section – slide number, labelled Slide Number Area. Field name is <number>.
The default footer fields are set up as follows using the Header and Footer dialog (Figure 18):
1) Select View > Master Slide from the Menu bar to open the master slide view. This also opens the Master View toolbar.
2) Select the master slide so that it appears in the Workspace.
3) Go to Insert > Header and Footer on the Menu bar to open the Header and Footer dialog.
Figure 18: Header and Footer dialog
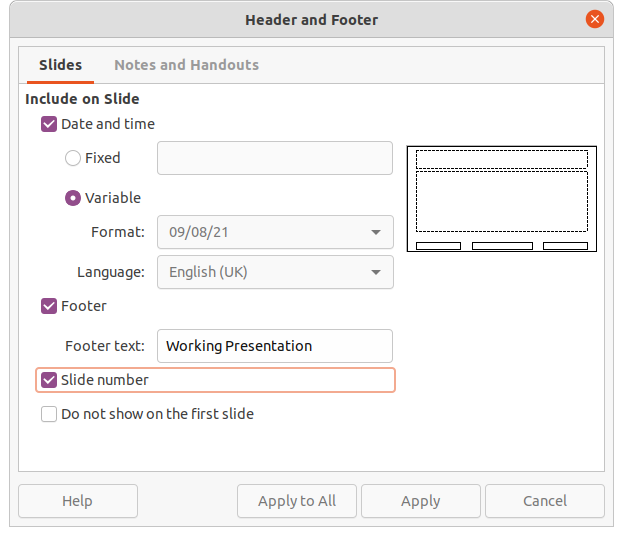
4) Select Date and Time for the date and time to appear in the left section of the footer.
For a fixed date and time in the left footer section, select Fixed and enter the date you want to use in the text box.
For a variable date and time in the left footer section, select Variable, then select the format and language to use from the Format and Language drop down lists. Using a variable date and time means that each time the presentation is opened, the date and time are updated.
5) To place text in the footer center section, select Footer and then type or paste the required text into the Footer text box.
6) To place the slide number in the right section of the footer, select Slide number.
7) If the footer is not going to appear on the first slide of a presentation, select Do not show on the first slide. The first slide is normally the title slide of a presentation.
8) Click Apply to save the changes and close the Header and Footer dialog.
9) To format the text used for the default footer fields, see Chapter 3, Adding and Formatting Text for more information.
10) Click Close Master View on the Master View toolbar or go to View > Normal on the Menu bar when setting up the default footer fields is completed.
Note
It is possible to format, resize, and reposition the default sections of a footer. See “Default text areas” and Chapter 3, Adding and Formatting Text for more information.
The default fields in a footer section can be replaced with text or manual fields as follows:
1) Select View > Master Slide from the Menu bar to open the master slide view. This also opens the Master View toolbar.
2) Select the master slide so that it appears in the Workspace.
3) Highlight the default field in the footer section and press the Delete or Backspace key. A flashing text cursor appears in the footer section and the Text Formatting toolbar automatically opens replacing the Line and Filling toolbar.
4) Type in the text or insert a manual field into the footer section. For more information on manual fields, see “Manual fields” below.
5) Format the text or manual field placed in the footer section. See Chapter 3, Adding and Formatting Text for more information.
6) Click outside the footer section to close the Text Formatting toolbar and reopen the Line and Filling toolbar.
7) Click Close Master View on the Master View toolbar or go to View > Normal on the Menu bar when setting up a custom footer section is completed.
Manual fields, for example date or slide number, can be added as text objects on a master slide or replace one of the default footer fields. The fields used in Impress are as follows:
Date (fixed)
Date (variable) – updates automatically each time the presentation is opened.
Time (fixed)
Time (variable) – updates automatically each time the presentation is opened and each time a slide is opened more than once during a presentation.
Author – first and last names listed in the LibreOffice user data.
Slide number
Slide Title
Slide Count
File Name
Inserting a field on a master slide is as follows:
1) Select View > Master Slide from the Menu bar to open the master slide view. This also opens the Master View toolbar.
2) Select the master slide so that it appears in the Workspace.
3) Click anywhere on the master slide without selecting an object.
4) Go to Insert > Field on the Menu bar and select the required field from the context menu and, by default, the field is placed in the center of the master slide.
5) Reposition the field text box to the desired position on the master slide. See “Default text areas” for more information.
6) Format the text placed in a field, see Chapter 3 Adding and Formatting Text for more information.
7) Click Close Master View on the Master View toolbar or go to View > Normal on the Menu bar when inserting a field is completed.
Replacing a default footer field on a master slide is as follows:
1) Select View > Master Slide from the Menu bar to open the master slide view. This also opens the Master View toolbar.
2) Select the master slide so that it appears in the Workspace.
3) Highlight all of the characters used in the default field being replaced in the footer.
4) Go to Insert > Field on the Menu bar and select the required field from the context menu.
5) Format the text placed in the field, see Chapter 3 Adding and Formatting Text for more information.
6) Click Close Master View on the Master View toolbar or go to View > Normal on the Menu bar when replacing the default footer fields is completed
Tip
To change the number format (1, 2, 3 or a, b, c or i, ii, iii, and so on) for the slide number, go to Slide > Slide Properties on the Menu bar to open the Slide Properties dialog. In Layout Settings, select the type of number format to use from the Slide numbers drop down list.
To change the author information, go to Tools > Options > LibreOffice > User Data on the Menu bar.
A style is a set of formats that can be applied to selected elements such as slides, text, lists, frames, borders, lines and area fills in a presentation to quickly set or change their appearance. Applying a style means applying a group of formats at the same time providing a consistent look to a presentation. For example, to manually change an attribute on the same object type on every slide in a presentation is time consuming and prone to errors. Using styles reduces time and provides greater accuracy.
Impress has two types of styles available for formatting text and graphic objects – presentation styles and drawing styles.
For information on formatting text, see Chapter 3, Adding and Formatting Text.
For information on formatting graphic objects, see Chapter 6, Formatting Graphic Objects and the Draw Guide.
More information on styles used in LibreOffice can be found in the Getting Started Guide.
Note
The presence of text and title styles both in the presentation and drawing styles may seem confusing. This apparent duplication is because Impress uses special text boxes (auto layout boxes) when adding structured text to slides where presentation styles apply. The title and other text styles in drawing styles are used on any other text boxes, or text associated with shapes or lines.
Presentation styles in Impress are used when creating a presentation using one of the Impress slide layouts. These presentation styles are divided into four categories.
Background and Background objects – are used to format objects on the default master slide such as icons, decorative lines, and shapes.
Notes – formats the text used in presentation notes.
Outline 1 thru Outline 9 – are used for the different levels of the outline to which they belong. For example, Outline 2 is used for the sub-points of Outline 1, Outline 3 is used for the sub-points of Outline 2 and so on.
Subtitle and Title – formats the text used for any titles or subtitles used on slides.
Note
As with the Heading styles in Writer, the Outline styles in Impress are hierarchically linked. For example, changing an attribute in the Outline 1 style cascades through all the other styles for Outline levels.
The default master slide and slide layouts in Impress use auto layout boxes. Presentation styles can only be used within these auto layout boxes. An example of text using these presentation styles is shown in Figure 2.
Note
Any text added to a slide using the text tools available is automatically placed in a standard text box and allocated the Default Drawing Style from Drawing Styles. For more information on formatting text, see Chapter 3, Adding and Formatting Text.
Presentation styles cannot be created or deleted, but can be formatted, modified or updated to the presentation requirements. Also, the presentation style used for an object cannot be changed to another presentation style. For example, text with Outline 2 style cannot be changed to Outline 3 style.
Note
Changing outline levels is done in normal view using the Tab key or Shift+Tab key combination or the Promote and Demote tools on the Outline toolbar. See Chapter 3, Adding and Formatting Text for more information.
Drawing styles in Impress define the characteristics of graphic objects (including text objects) placed on a slide. These styles include attributes for line, area, shadowing, transparency, text, connectors and dimensioning.
For example, when creating organization charts in a presentation, it will probably be required to have all of the objects with a consistent appearance, such as line style, font type, shadow, and so on. The easiest way to achieve this result with the minimum effort is to use a drawing style for the objects and apply it to each object. The major benefit is that if there is a change, say, the background color of objects, all that is required is to modify the style rather than each individual object.
Drawing styles included with Impress cannot be deleted, but can be formatted, modified, and updated. Also new or custom styles can be created, see “Custom styles”. Any custom style created is only available in the presentation where it was created.
Use one of the following methods to access or modify styles available in Impress:
Use the keyboard shortcut F11 (Windows and Linux) or ⌘+T (macOS).
Go to Format > Styles on the Menu bar.
Click on Show the Styles Sidebar (F11) located on the Line and Filling toolbar.
Click on Styles on the Sidebar to open the Styles deck.
Formatting presentation and drawing styles can be carried out in either Normal or Master Slide view. Formatting options are available in dialogs for each style or using Format in the Menu bar. For more information on formatting text and objects, see Chapter 3, Adding and Formatting Text and Chapter 6, Formatting Graphic Objects.
1) Select an object on a slide or master slide and its style is highlighted in the Styles deck on the Sidebar.
2) Go to Format > Styles > Edit Style on the Menu bar or right-click on the highlighted style in the Styles deck on the Sidebar to open the formatting dialog for the selected style. An example dialog for the Title style is shown in Figure 19.
3) Use the various options available in the tabbed pages of the dialog to format the style.
4) Click OK to save the formatting changes and close the dialog.
Figure 19: Example dialog for formatting styles
Note
Clicking on Reset before clicking OK removes all formatting changes made in the style formatting dialog.
1) Open the Styles deck on the Sidebar. See “Accessing styles” for more information.
2) Click on Presentation Styles or Drawing Styles at the top left of the Styles deck and select a style from the displayed list.
3) Go to Format on the Menu bar to open a submenu with various formatting options available. Depending on the object selected, some formatting options will not be available and are greyed out.
4) Select a formatting option from the submenu. Depending on the option selected, another submenu may open giving further formatting options or a formatting dialog opens.
1) Open the Styles deck on the Sidebar. See “Accessing styles” for more information.
2) Click on Presentation Styles or Drawing Styles at the top left of the Styles deck and select a style from the displayed list.
3) Right-click on the style selected and select Modify from the context menu to open the formatting dialog for the style selected. An example dialog for the Title style is shown in Figure 19.
4) Make the necessary changes to the selected style using the various options available in the dialog that has opened.
5) Click OK to save the changes and close the dialog.
Updating a presentation or drawing style is similar to modifying, but changes to the text or object are made first. Updating styles can only be carried out in Normal view.
1) Select the text or object on a slide in Normal view.
2) Use the various tools on the Text Formatting toolbar, Line and Filling toolbar, or the options in Format on the Menu bar to format the selected object.
3) Open the Styles deck on the Sidebar. See “Accessing styles” for more information.
4) Click on Presentation Styles or Drawing Styles at the top left of the Styles deck and select a style from the displayed list. The style used for the selected object will be highlighted.
5) Click on Update Style at the top right of the Styles deck and the style is updated to include the formatting changes made to the selected object.
Custom presentation styles cannot be created in Impress, only custom drawing styles can be created. These custom drawing styles are only available for the presentation being created.
1) Create or select an object on a slide to create a custom drawing style.
Figure 20: New Style from Selection dialog
2) Format the object to the presentation requirements using the various formatting options available in the Text Formatting toolbar, Line and Filling toolbar, or the options in Format on the Menu bar.
3) Open the Styles deck on the Sidebar. See “Accessing styles” for more information.
4) Click on Drawing Styles at the top left of the Styles deck to open the drawing styles list.
5) Click on New Style from Selection at the top right of the Styles deck and the New Style from Selection dialog opens (Figure 20).
6) Enter a name for the custom drawing style in the Enter new style name text box.
7) Click OK to close the Create Style dialog. The custom drawing style is created and appears in the drawing styles list in the Styles deck on the Sidebar.
Direct formatting overrides any formatting applied to an object when a style is used. Direct formatting cannot be removed from an object by applying a style to it. To remove any direct formatting, select the object so that the selection handles are visible, then use one of the following methods to clear any direct formatting:
Use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Shift+M.
Go to Format > Clear Direct Formatting in the Menu bar.
If the object is a text object, highlight all of the text and then click on Clear Direct Formatting on the Text Formatting toolbar.
If the object is a text object, highlight all of the text, right-click on the selected text and select Clear Direct Formatting from the context menu.
Impress styles support linking or inheritance. This allows a style to be linked to another (parent) style so that it inherits all the formatting settings of the parent, creating families of styles.
For example, if there are multiple boxes that differ in color, but are otherwise identically formatted, the best way to proceed is to define a style for the box including borders, area fill, font, and so on. Then create a number of styles that are hierarchically dependent, but differ only in the fill color attribute. For example, if the font size or the thickness of the border needs to be changed, only change the parent style and all the other linked (child) styles change accordingly.
LibreOffice provides a set of predefined keyboard shortcuts which allow quick application of styles while working with a presentation. These shortcuts can be redefined or custom shortcuts created. For more information, see Appendix A, Keyboard Shortcuts and the Getting Started Guide.
A template is a special type of presentation that used as a basis to create presentations. For example, create a template for business presentations so that any new presentations have the company logo, name and information on the first slide and the remaining slides in the presentation only show the company logo and name.
Figure 21: Select a Template dialog
Templates can contain anything that presentations can contain, such as text, graphics, a set of styles, and user-specific setup information such as measurement units, language, the default printer, and toolbar and menu customization.
All document types created using LibreOffice are based on templates. Specific templates can be created for any document type (text, spreadsheet, drawing, presentation). If a template is not specified when creating a new document, then the default template for that type of document is used. If a default template is not specified, LibreOffice uses the blank template for that type of document that is installed with LibreOffice. This default template can be changed, see “Setting default template” for more information.
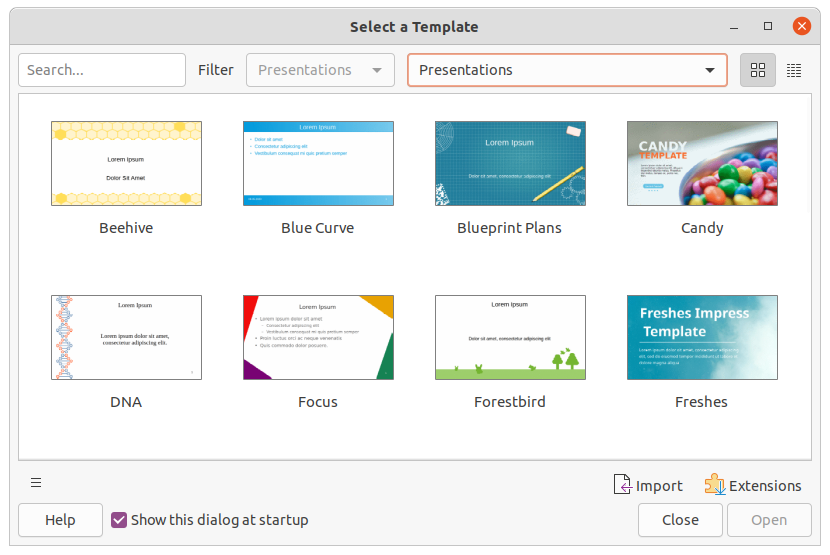
However, Impress is a little different from other LibreOffice components, in that it starts with the Select a Template dialog (Figure 21), unless this option has been turned off for this dialog in LibreOffice options. When creating a presentation and the template dialog is active, it opens offering several choices for templates as a starting point for a presentation. If this Select a Template dialog is turned off for creating a new presentation, LibreOffice uses the LibreOffice default template for presentations. If a default template has been defined, LibreOffice uses this default template to create a presentation, see “Setting default template” for more information.
For more information on templates and how to use them, see the Getting Started Guide.
Impress comes with a set of predefined templates. These templates only contain backgrounds and background objects, providing a starting point to create presentations or presentation templates.
Any templates created are located in the My Templates folder after the template has been saved as a presentation template. These templates appear in the LibreOffice startup window and the Select a Template dialog the next time LibreOffice is started.
Use one of the following methods to create a new presentation using a template:
Click on the small triangle ▼ on the right of Templates in LibreOffice start up window and then select Impress Templates from the context menu to display the available presentation templates. Select a template and a new presentation opens.
Go to File > New > Templates on the Menu bar to open the Templates dialog (this dialog is similar to the Select a Template dialog). Select Presentations from the Filter drop‑down list to display presentation templates. Select a presentation template and click OK. The dialog closes and a new presentation opens.
Use the keyboard shortcut Shift+Ctrl+N to open the Templates dialog (this dialog is similar to the Select a Template dialog). Select Presentations from the Filter drop-down list to display presentation templates. Select a presentation template and click OK. The dialog closes and a new presentation opens.
Create a template and save it to a template folder as follows:
1) Open a presentation or presentation template as a starting point for a new template.
2) Add and format the content and styles as required for the new presentation template.
3) Go to File > Templates > Save As Template on the Menu bar to open the Save as Template dialog (Figure 22).
4) Enter a name for the new template in the Enter Template Name text box.
5) Select a template category for the new template.
Figure 22: Save As Template dialog
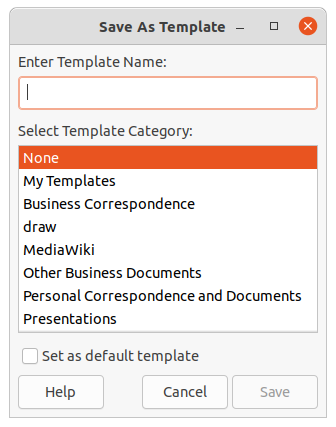
6) If required, select the option Set as default template to use as the default template the next time LibreOffice is opened and no template is selected. See “Setting default template” below for more information on setting default templates.
7) Click on Save to save the new template and close the Save as Template dialog. The template will appear in the LibreOffice startup window and the Select a Template dialog the next time LibreOffice is started.
Note
When saving a new template, it is important to save the template in one of the categories given in the Save as Template dialog. This allows LibreOffice to find the new template and use it for creating a new presentation.
If a new presentation is being created and no template is selected, LibreOffice creates the presentation from the default Impress template. This is normally a blank template. However, any presentation template can be set as the default template, even a template that has been created. The template has to be located in a category displayed in the Save as Template dialog so that LibreOffice can find it. The default template can always be reset to the original LibreOffice default template.
1) Use one of the following methods to open the Select a Template dialog.
Go to File > New > Templates on the Menu bar.
Go to File > Templates > Manage Templates on the Menu bar.
2) Select the template to use as the default LibreOffice presentation template.
3) Right-click on the selected template and select Set as Default from the context menu.
4) Click on Open and a new presentation opens using the new default template and sets the default presentation template in LibreOffice. The next time a new presentation is created and a template is not selected, the presentation is created using the new default presentation template.
To reset the default presentation template back to the original LibreOffice default template for presentations:
1) Use one of the following methods to open the Select a Template dialog.
Go to File > New > Templates on the Menu bar.
Go to File > Templates > Manage Templates on the Menu bar.
2) Select the presentation template that is being used as the default presentation template in the Select a Template dialog.
3) Right-click on the template and select Reset Default from the context menu.
4) Click on Close to close the Select a Template dialog. The next time that a new presentation is created and a template is not selected, the presentation is created using the default LibreOffice presentation template.
Template styles and content can be edited and reapplied to presentations that were created from that template.
1) Use one of the following methods to open the Select a Template dialog.
Go to File > New > Templates on the Menu bar.
Go to File > Templates > Manage Templates on the Menu bar.
Click on the small triangle ▼ on the right of Templates in LibreOffice start up window and select Impress Templates from the context menu.
2) Right-click on the template to be edited and select Edit from the context menu and the template opens in Impress.
3) Edit and update the styles, text and/or objects on the selected template.
4) Go to File > Save on the Menu bar or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+S to save your changes.
5) Close the template or create a presentation using the edited template.
Note
Any presentation created from the template before editing can be updated to show the changed template settings the next time the presentation is opened after template editing. A confirmation dialog opens asking if the updated styles are to be used or keep the old styles. If keep the old styles is selected, then the presentation continues to use the old styles without any confirmation.
LibreOffice can only use templates that are in LibreOffice template categories (template folders). New LibreOffice template categories can be created and used to organize LibreOffice templates. For example, separate template categories for different projects or clients. Templates can also be imported and exported.
Tip
The location of folders used LibreOffice template categories varies with computer operating systems. To learn where the template folders are stored on a computer, go to Tools > Options > LibreOffice > Paths.
1) Use one of the following methods to open the Select a Template dialog.
Go to File > New > Templates on the Menu bar.
Go to File > Templates > Manage Templates on the Menu bar.
2) Right-click on Tools in the bottom left of the Select a Template dialog and select New Category from the context menu.
3) Enter a category name in Enter new category name box that has opened.
4) Click OK to save the new category and the category appears in the Filter drop-down list for categories at the top of the Select a Template dialog.
Figure 23: Delete Category dialog
Template categories supplied with LibreOffice or installed using the Extension Manager cannot be deleted. Only custom categories that have been created in Impress can be deleted.
1) Use one of the following methods to open the Select a Template dialog.
Go to File > New > Templates on the Menu bar.
Go to File > Templates > Manage Templates on the Menu bar.
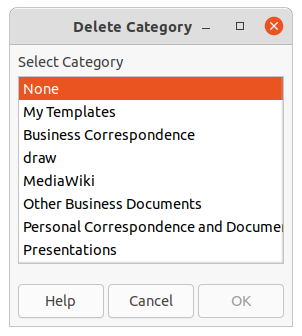
2) Right-click on Tools in the bottom left of the Select a Template dialog.
3) Select Delete Category from the context menu to open the Delete Category dialog (Figure 23).
4) Select the custom category for deletion.
5) Click OK to delete the custom category and confirm the deletion.
1) Use one of the following methods to open the Select a Template dialog.
Go to File > New > Templates on the Menu bar.
Go to File > Templates > Manage Templates on the Menu bar.
2) Select the template that is going to be moved.
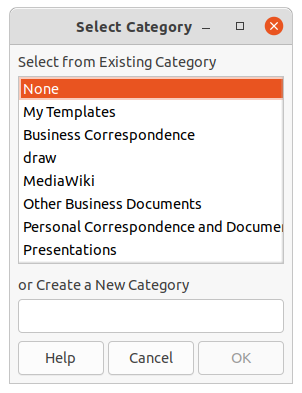
3) Click on Move at the bottom of the Select a Template dialog to open the Select Category dialog (Figure 24).
4) Select a category from the displayed list in Select from Existing Category, or select Create a New Category and create a new category for the template.
5) Click OK to move the template to its new category and close the Select Category dialog.
Figure 24: Select Category dialog
Templates supplied with LibreOffice or installed using the Extension Manager cannot be deleted. Only templates that have been created in Impress or imported from other sources can be deleted.
1) Use one of the following methods to open the Select a Template dialog.
Go to File > New > Templates on the Menu bar.
Go to File > Templates > Manage Templates on the Menu bar.
2) Right-click on the template being deleted and select Delete from the context menu.
3) Click on Yes to confirm the deletion.
Templates supplied with LibreOffice or installed using the Extension Manager cannot be renamed. Only templates that have been created in Impress or imported from other sources can be renamed.
1) Use one of the following methods to open the Select a Template dialog.
Go to File > New > Templates on the Menu bar.
Go to File > Templates > Manage Templates on the Menu bar.
2) Right-click on the template being renamed and select Rename from the context menu.
3) Enter a new template name in the text box that has opened.
4) Click on OK to save the new template name.
If a template is in a different location on the computer, then the template must be imported into a LibreOffice category for LibreOffice to recognize the template.
1) Use one of the following methods to open the Select a Template dialog.
Go to File > New > Templates on the Menu bar.
Go to File > Templates > Manage Templates on the Menu bar.
2) Click on Import at the bottom of the Select a Template dialog to open the Select Category dialog.
3) Select a category from the displayed list or select Create a New Category in the Select Category dialog.
4) In the file browser window that opens, navigate to the folder where the template is located on the computer.
5) Select the template and click Open. The file browser window closes and the template appears in the selected category.
1) Use one of the following methods to open the Select a Template dialog.
Go to File > New > Templates on the Menu bar.
Go to File > Templates > Manage Templates on the Menu bar.
2) Select the template for export, then click on Export at the bottom of the Select a Template dialog to open a file browser window.
3) Navigate to the folder where the template is to be exported to and click on OK. The template is exported to the selected location and the file browser window closes.