Impress Guide 7.3
Chapter 12,
User Interface Variants
This document is Copyright © 2022 by the LibreOffice Documentation Team. Contributors are listed below. This document maybe distributed and/or modified under the terms of either the GNU General Public License (https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html), version 3 or later, or the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), version 4.0 or later.
All trademarks within this guide belong to their legitimate owners.
|
Peter Schofield |
Kees Kriek |
|
|
Peter Schofield |
Vasudev Narayanan |
Rachel Kartch |
Please direct any comments or suggestions about this document to the Documentation Team’s mailing list: documentation@global.libreoffice.org
Note
Everything sent to a mailing list, including email addresses and any other personal information that is written in the message, is publicly archived and cannot be deleted.
Published May 2022. Based on LibreOffice 7.3 Community.
Other versions of LibreOffice may differ in appearance and functionality.
Some keystrokes and menu items are different on macOS from those used in Windows and Linux. The table below gives some common substitutions for the instructions in this document. For a detailed list, see the application Help.
|
Windows or Linux |
macOS equivalent |
Effect |
|
Tools > Options on Menu bar |
LibreOffice > Preferences on Menu bar |
Access to setup options |
|
Right-click |
Ctrl+click and/or right-click depending on computer setup |
Opens a context menu |
|
Ctrl or Control |
⌘ and/or Cmd or Command |
|
|
Alt |
⌥ and/or Alt or Option |
Used with other keys |
|
F11 |
⌘+T |
Open the Styles deck in the Sidebar |
By default, commands and tools used in LibreOffice Impress are grouped in a user interface consisting of cascading menus and toolbars. The functions and use of these cascading menus and toolbars are described in previous chapters of this user guide.
This chapter describes the user interface variants that are available for LibreOffice Impress. A user then has the option to select the user interface that suits their requirements and methods of creating presentations in LibreOffice Impress.
Note
When changing the user interface, the variant can be applied only to LibreOffice Impress, or applied to all the modules in LibreOffice.
To select a user interface variant or switch between the user interface variants:
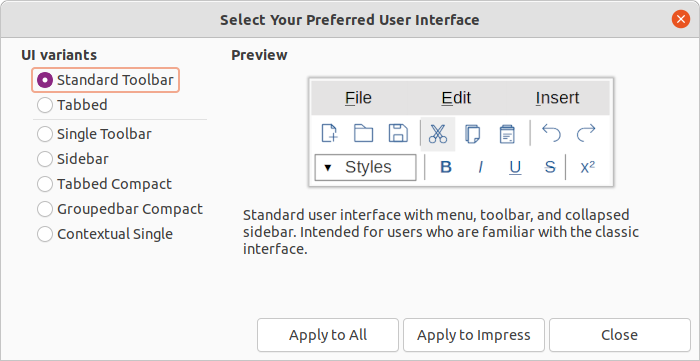
1) Go to View > User Interface on the Menu bar to open the Select Your Preferred User Interface dialog (Figure 1).
2) In UI variants, select one of the variants. An example of the selected variant is shown in the Preview box, along with a short description.
3) Click on Apply to Impress to apply the variant selection to LibreOffice Impress only, or click on Apply to All to apply the user interface variant to all the LibreOffice modules. The LibreOffice window changes to match the selected variant.
4) Click Close to close the dialog.
Figure 1: Select Your Preferred User Interface Variant dialog
Note
If the option Enable experimental features has been selected in the Tools > Options > Advanced dialog, several more variants appear in UI variants. Being experimental, these variants are not described in this user guide.
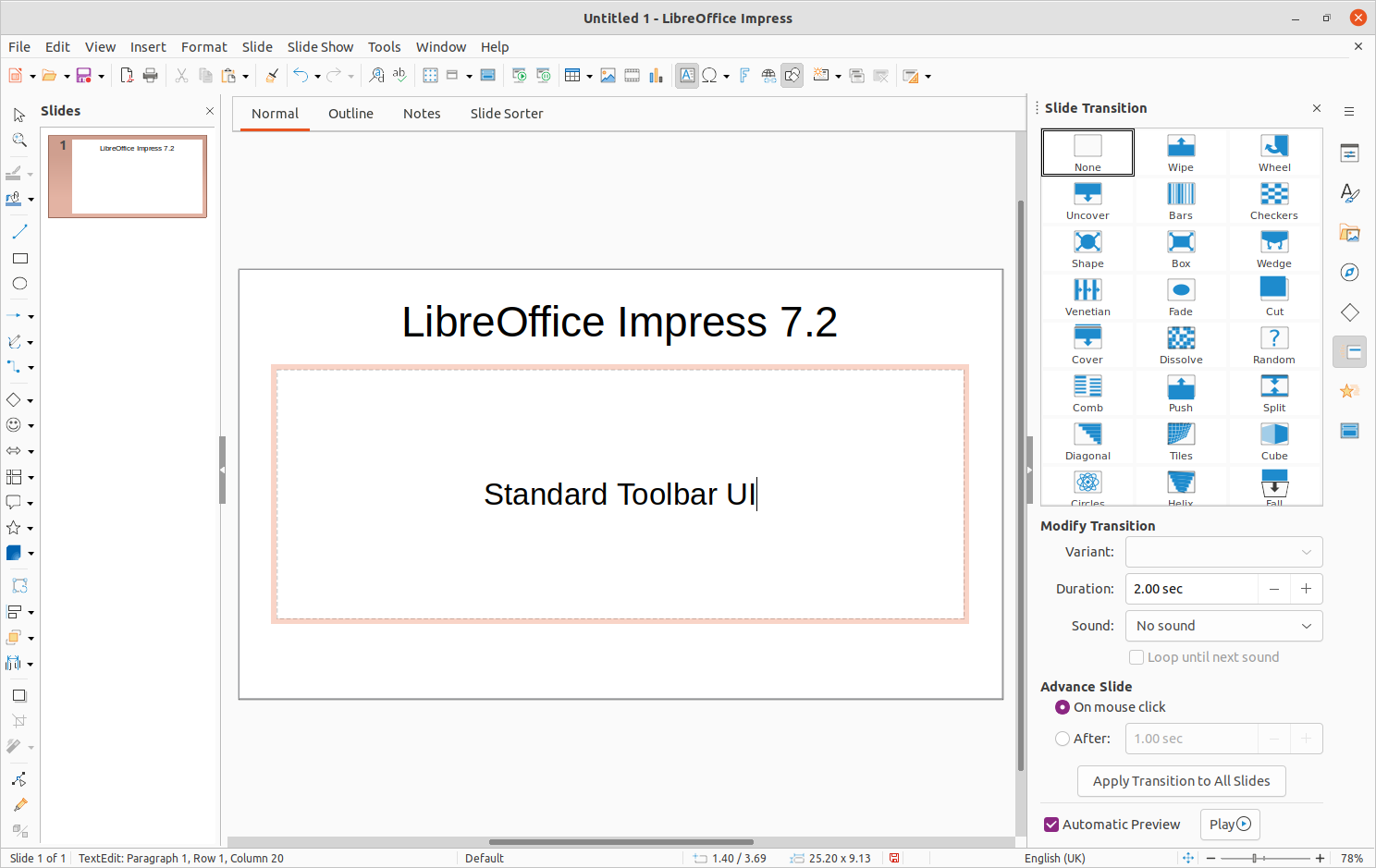
Figure 2: Standard Toolbar user interface in LibreOffice Impress
Note
In all the user interface variants, the Sidebar can be hidden or shown by clicking on the Hide/Show button on the left of the Sidebar,
The Standard Toolbar user interface is the default view when LibreOffice is installed and the Workspace opened for the first time. Figure 2 shows an example of the default Workspace view in LibreOffice Impress consisting of the following:
Menu bar at the top of the Workspace.
Standard toolbar positioned below the Menu bar.
Drawing toolbar positioned vertically on the left of the Workspace.
Sidebar on the right of the Workspace.
For more information on the Impress Workspace, see Chapter 1, Introducing Impress.
The Tabbed user interface provides a familiar interface for users coming from proprietary office suites, for example, Microsoft Office. Every tab within this user interface consists of a set of tools grouped by context. The context changes automatically depending on the LibreOffice module and the object selected.
It includes a Menu bar, a Tab bar, and tool icons grouped in context that would be normally used in LibreOffice Impress. If the tool icons on a tab page do not fit into the width of the Impress window, a double chevron >> appears at the right end of the row. Click the double chevron >> to display more commands.
Figure 3: Quick menu options
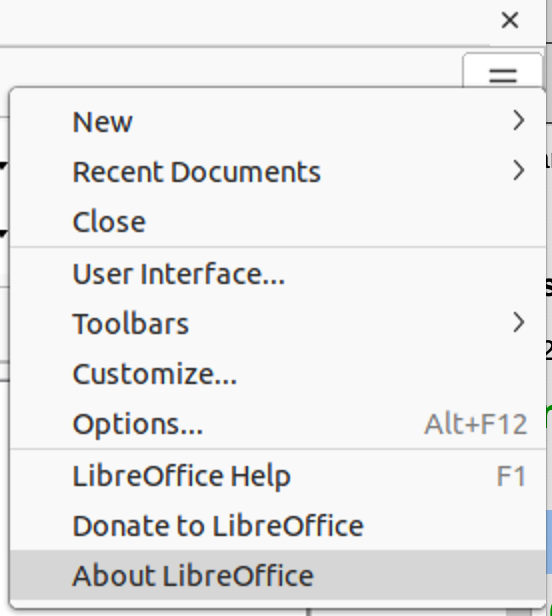
Figure 4: Icon bar
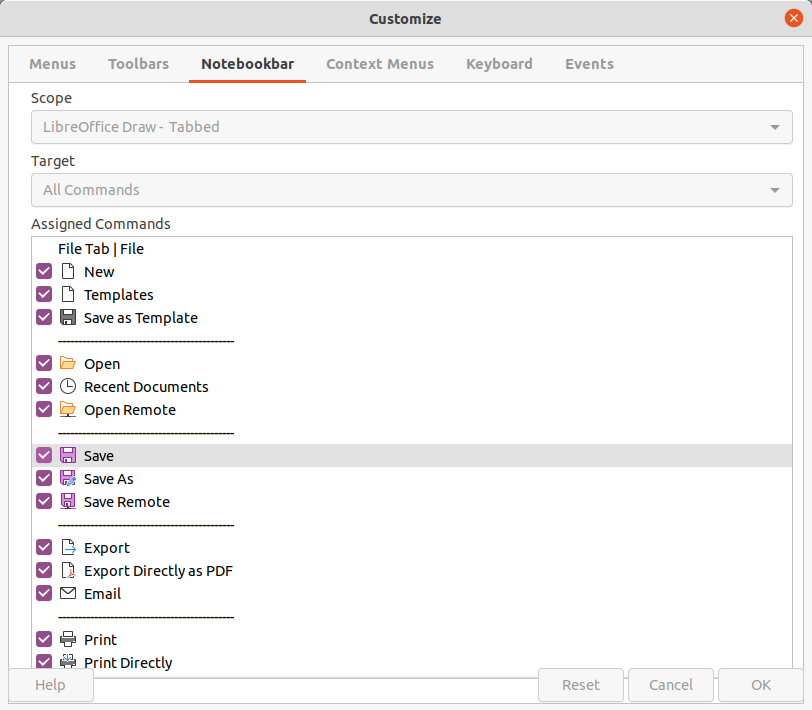
Figure 5: Customize dialog - Notebookbar page
On Windows and Linux operating systems, the Menu bar can be hidden or displayed by clicking on Menubar at the left end of the Tab bar.
On the right of the Tab bar, a Quick menu (≡) (Figure 3) is available giving access to some commonly used commands and links. Some of the Quick menu items have submenus, indicated by a small triangle ► on the right. The Quick menu is the same for all tabs.
On the left of the Tab bar, an Icon bar (Figure 4) is available giving access to some commonly used tools – Menubar; Open (Ctrl+O); Save (Ctrl+S);Undo (Ctrl+Z); Redo (Ctrl+Y); Start from First Slide (F5).
The Tabbed user interface can be customized using the Notebookbar page of the Customize dialog (Figure 5) to show or hide the individual tools on the various tabs. For more information on customization of LibreOffice, see the Getting Started Guide and the Writer Guide.
Note
When using the Tabbed user interface, the Impress toolbars are no longer visible. If necessary, it is possible to open toolbars by going to View > Toolbars on the Menu bar or Quick menu > Toolbars.
The fixed tabs in the Tabbed user interface for Impress are described on the following pages. The following figures show the left and right ends of the tabs separately so they are large enough to more easily see the commands.
The File tab (Figure 6) is a fixed tab providing commands to create new documents; open, save, print, and close documents; manage templates; export to PDF and EPUB; display document properties; add a digital signature; and sign an existing PDF.
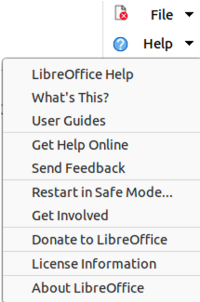
The File tab has two menus (Figures 7 and 8): File and Help. The File tab menu contains the same commands as the tools available on the tab. The Help tab menu provides links to a variety of resources.
Figure 6: Tabbed user interface - File tab
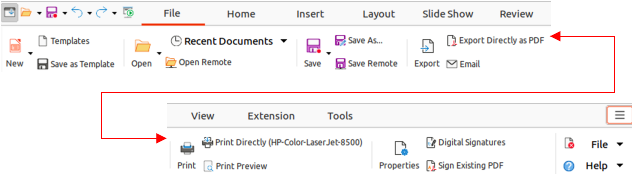
Figure 7: File tab - File menu
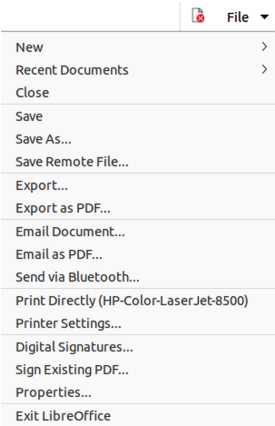
Figure 8: File tab - Help menu
The Home tab (Figure 9) is a fixed tab providing commands to cut, copy, paste, and format text; insert common items (for example images, tables, charts); apply, update, and edit drawing styles; and so on. The Home menu (Figure 10) at the right end of the Home tab bar provides additional tools that are not on the tab.
Figure 9: Tabbed user interface - Home tab
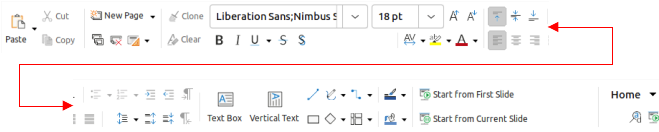
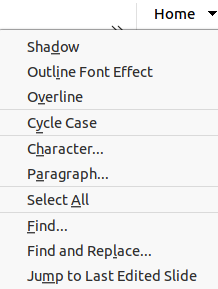
Figure 10: Home tab - Home menu
The Insert tab (Figure 11) is a fixed tab providing tools to insert many commonly used items. The Insert menu (Figure 12) at the right end of the Insert tab bar provides some of the same tools.
Figure 11: Tabbed user interface - Insert tab
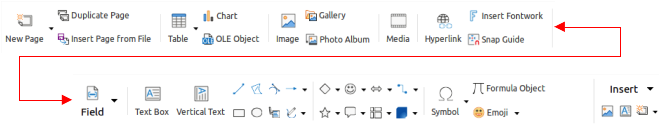
Figure 12: Insert tab - Insert menu
The Layout tab (Figure 13) is a fixed tab providing tools to create a slide layout. The Layout menu (Figure 14) at the right end of the Layout tab bar provides some of the same tools.
Figure 13: Tabbed user interface - Layout tab
Figure 14: Layout tab – Layout menu
Figure 15: Tabbed user interface - Slide Show tab
Figure 16: Slide Show tab - Slide Show menu
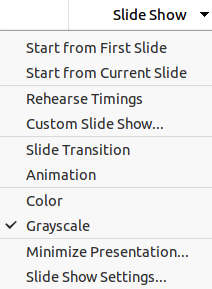
The Slide Show tab (Figure 15) is a fixed tab providing tools for creating a slide show. The Slide Show menu (Figure 16) at the right end of the Slide Show tab bar provides some of the same tools.
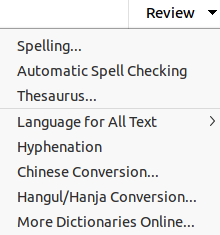
The Review tab (Figure 17) is a fixed tab providing tools for reviewing a slide show. The Review menu (Figure 18) provides additional text editing tools. Some of these tools appear only if Asian or Complex Text Layout are selected in Tools > Options > Language Settings > Languages.
Figure 17: Tabbed user interface - Review tab
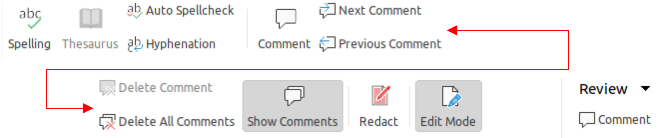
Figure 18: Review tab - Review menu
The View tab (Figure 19) is a fixed tab providing tools to control the display of slides on a screen. The View menu (Figure 20) provides additional tools relating to the display of slides on a screen.
Figure 19: Tabbed user interface - View tab
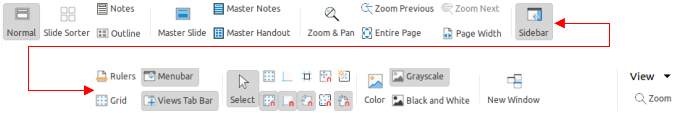
Figure 20: View tab - View menu
The Extension tab (Figure 21) is a fixed tab containing only the tool to access the Extension Manager allowing the installation of extensions that are compatible for use in LibreOffice.
Figure 21: Tabbed user interface - Extension tab
The Tools tab (Figure 22) is a fixed tab providing several tools for macros; color replacer; media player; and so on. The Tools menu (Figure 23) provides some of the same tools, plus extra tools for organizing, for example, macros and dialogs; image map; data sources; and so on.
Figure 22: Tabbed user interface - Tools tab
Figure 23: Tools tab - Tools menu
Additional tabs appear between the View and Extension tabs when an object in Impress is selected. The illustrations show the left and right ends of the tabs separately so they are large enough to more easily see the commands.
The Draw tab (Figure 24) becomes available when a drawing object is selected in a slide. It provides tools for editing, transforming, grouping, aligning, and distributing draw objects. The Draw tab menu (Figure 25) provides some of the tools required for editing, transforming and converting drawing objects.
Figure 24: Tabbed user interface - Draw tab
Figure 25: Draw tab - Draw menu
The Image tab (Figure 26) becomes available when an image is selected in a slide, for example a photograph. It provides tools for working with images, such as cropping, borders, area styles, colors, and so on. The Image tab menu (Figure 27) provides links to dialogs for working with images.
Figure 26: Tabbed user interface - Image tab
Figure 27: Image tab - Image menu
The Object tab (Figure 28) becomes available when an object, such as a chart, is selected. It provides tools to position, resize, choose colors, and so on for the selected object. The Object tab menu (Figure 29) provides extra tools matching the type of object selected.
Figure 28: Tabbed user interface - Object tab
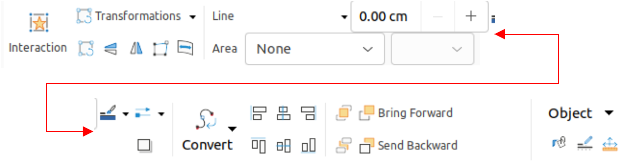
Figure 29: Object tab - Object menu
The Table tab (Figure 30) becomes available when a table is selected in a slide. It provides tools to format a table to the presentation requirements. The Table tab menu (Figure 31) includes extra tools for editing a table.
Figure 30: Tabbed user interface - Table tab
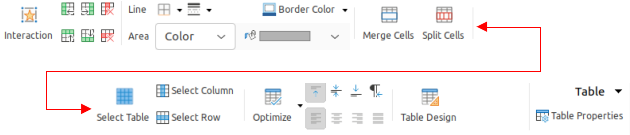
Figure 31: Table tab - Table menu
The Media tab (Figure 32) only becomes available when a media object is selected in a slide. It provides tools for positioning and running an audio or video file. The Media tab menu (Figure 33) includes extra tools for editing a media object.
Figure 32: Tabbed user interface - Media tab
Figure 33: Media tab - Media menu
When selected, the Single Toolbar and Sidebar user interfaces only show the Menu bar with no toolbars. However, toolbars can be added to either of these user interfaces by going to View > Toolbars on the Menu bar and selecting the required toolbar from the options available. For more information on toolbars, see Appendix B, Toolbars in this guide and the Getting Started Guide.
The Tabbed Compact user interface has the same tabs as the Tabbed user interface, but the tools on each tab are arranged as a single row of tools. Some of these tools have drop‑down menus with extra options. Figure 34 shows an example of the File tab in the Tabbed Compact user interface.
The tab menu on the right of the Tabbed Compact user interface provides the same options as the tab menus in the Tabbed user interface, see “Tabbed UI” on page 1 for more information.
Figure 34: Example of Tabbed Compact user interface showing File tab
The Groupedbar Compact user interface is divided into groups that contain commands organized as sets of tools and menus. The tools and menus that are available change to suit the type of object selected. Clicking on the double chevron >> displays more tools for editing an object. Figure 35 shows an example of Groupedbar Compact user interface when a basic shape object is selected.
The Groupedbar Compact menu (Figure 36) on the right-hand end of this interface provides extra tools for working with LibreOffice Impress, including convenient ways to change the user interface and access toolbars.
Figure 35: Example of Groupedbar Compact user interface with an object selected
Figure 36: Menu for Groupedbar Compact UI
The Contextual Single user interface displays a single toolbar to suit the type of object that has been selected. Clicking on the double chevron >> displays more tools for editing an object. Figure 37 shows an example of a Contextual Single user interface when a basic shape object is selected.
Figure 37: Example of Contextual Single user interface with a basic shape selected